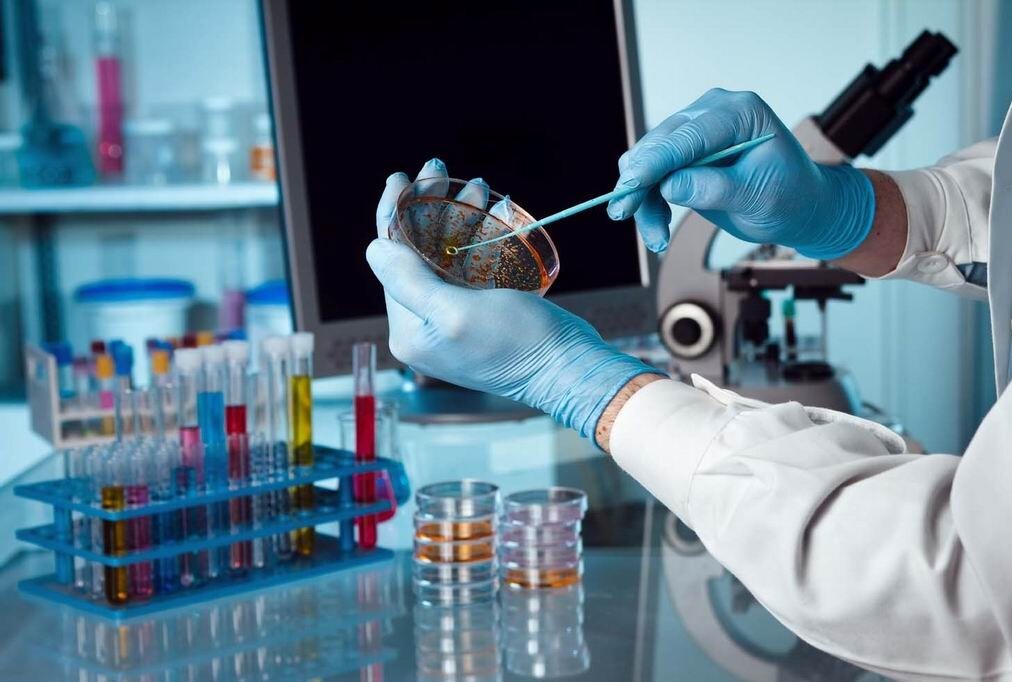
Microbiology laboratories play a crucial role in scientific research, healthcare, and various industries. These facilities are dedicated to the study and analysis of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and parasites. Understanding the fundamentals of microbiology laboratories is essential for appreciating their significance in advancing knowledge and addressing public health concerns.
Purpose of Microbiology Laboratories:
Microbiology laboratories serve diverse purposes, including:
- Disease Diagnosis: They aid in diagnosing infectious diseases by identifying the causative microorganisms in patient samples.
- Research: Microbiology laboratories facilitate research on various aspects of microorganisms, such as their genetics, physiology, and interactions.
- Quality Control: Industries like food and pharmaceuticals rely on microbiology laboratories to ensure product safety and quality by testing for microbial contamination.
- Environmental Monitoring: These labs assess microbial populations in environmental samples to monitor pollution levels and study ecosystem dynamics.
Infrastructure and Equipment:
Microbiology laboratories are equipped with specialized tools and facilities, including:
- Microscopes: High-powered microscopes are essential for observing microorganisms at the cellular and subcellular levels.
- Incubators: These maintain optimal temperature and humidity conditions for cultivating microorganisms.
- Biosafety Cabinets: These provide a sterile environment for handling potentially hazardous microorganisms, preventing contamination and protecting lab personnel.
- Culture Media: Nutrient-rich substances used to cultivate and grow microorganisms in controlled laboratory conditions.
- Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Machines: Vital for amplifying and analyzing DNA, enabling the detection of specific microorganisms or genetic markers.
Laboratory Techniques:
Microbiology laboratories employ various techniques for studying microorganisms, including:
- Microbial Culture: The process of isolating and growing microorganisms on culture media, allowing for their identification and study.
- Staining Techniques: Stains like Gram stain and acid-fast stain help differentiate between different types of bacteria based on their cell wall characteristics.
- Molecular Biology Methods: PCR, DNA sequencing, and other molecular techniques enable the identification and characterization of microorganisms based on their genetic material.
- Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing: Determines the susceptibility of bacterial isolates to different antibiotics, guiding treatment decisions in clinical settings.
Safety Protocols:
Given the potential risks associated with handling pathogenic microorganisms, microbiology laboratories adhere to strict safety protocols, including:
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE): Lab personnel wear gloves, lab coats, and goggles to minimize exposure to hazardous materials.
- Biosafety Levels (BSL): Laboratories are classified into different biosafety levels based on the level of risk posed by the microorganisms handled, with higher levels requiring more stringent safety measures.
- Decontamination Procedures: Surfaces and equipment are regularly disinfected to prevent cross-contamination and ensure a safe working environment.
Emerging Trends and Technologies:
Advancements in technology continue to revolutionize microbiology laboratories, with developments such as:
- Next-Generation Sequencing (NGS): Enables rapid and comprehensive analysis of microbial communities, facilitating metagenomics and microbiome research.
- CRISPR-Cas9 Gene Editing: Revolutionizes genetic manipulation of microorganisms, offering unprecedented precision and efficiency in genome engineering.
- Point-of-Care Testing: Portable diagnostic devices allow for rapid and on-site detection of microbial pathogens, enhancing disease surveillance and management.
In conclusion, microbiology laboratories are dynamic hubs of scientific inquiry and innovation, driving advancements in healthcare, agriculture, and biotechnology. By familiarizing ourselves with the fundamentals of these laboratories, we can appreciate their critical role in understanding and harnessing the potential of microorganisms for the betterment of society.
post by: roland.co.id